Published on: 18 March, 2021
Read Time: 3 min
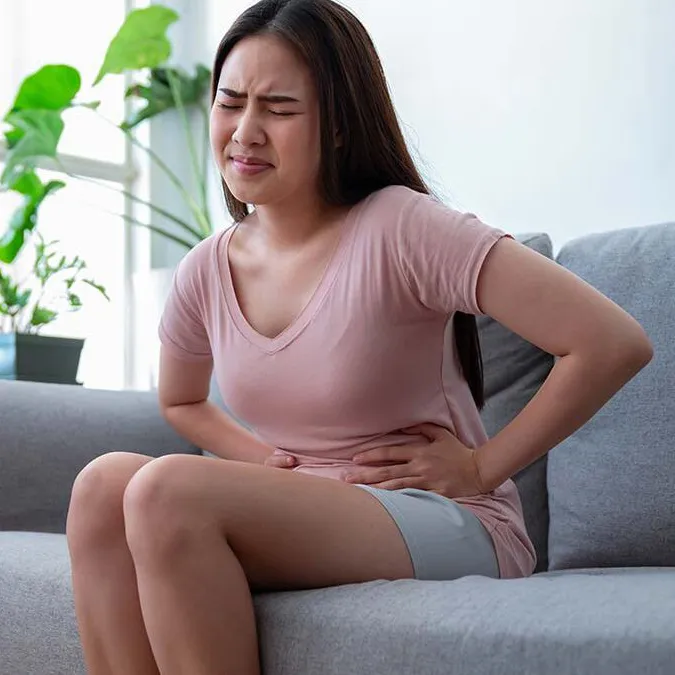
Painful and frequent urination are symptoms that are linked to the following medical conditions
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- Vaginitis
- STDs (ie. chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes)
These conditions are discussed in more detail below.
Urinary tract infections
It is estimated that around 60% of women will develop a urinary tract infection (UTI) at least once in their lifetimes. A UTI is a common infection that occurs in the lower urinary tract –the bladder and urethra.
Signs and symptoms
UTI’s do not always cause signs or symptoms. However, when symptoms do appear they usually include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Urine that appears cloudy in colour
- Strong-smelling urine
- Urine that appears red, bright pink or cola-colour — a sign of blood in the urine
Diagnosis
If you have noticed any of the symptoms above it is important to see your doctor as soon as possible. Left untreated, a UTI can spread up towards the kidneys and lead to more serious complications. Diagnosing a UTI may be done with a quick urine sample or based on your medical symptoms alone.
Treatment
Most urinary tract infections can be treated with a course of antibiotics. Your doctor may also speak to you about any previous UTIs, possible further testing and steps you can take to help prevent them from recurring.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis occurs when the vagina or vulva have an infection or irritation. This disruption in the normal environment of the vagina leads to some of symptoms that are experienced.
Symptoms of vaginitis
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal itching, burning
- Pain with sexual intercourse
- Painful urination
Vaginitis has both infective and non-infective causes. For a majority of affected women, vaginitis is caused by: Bacterial vaginosis, yeast (candidiasis) infections and trichomoniasis, a sexually transmitted infection.
- Bacterial vaginosis – a condition that results from a change of the normal bacteria found in the vagina. Essentially, good bacteria in the vagina are overgrown by bad bacteria. In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, the discharge of bacterial vaginosis appears thin white or gray. Bacterial vaginosis may resolve on its own or require antibiotics.
- Yeast infections – these are usually caused by a naturally occurring fungus called candida albicans. A vaginal yeast infection is a fungal infection that causes irritation, discharge (appears as thick, white, clumps) and intense itchiness of the vagina and the vulva. Treatment for a yeast infection can be sought by using over the counter medications that are available at most pharmacies.
- STI – STI’s such as Trichomoniasis may also cause vaginitis or irritation of the vagina.
Sexually transmitted infections
STI’s such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and herpes can produce a number of symptoms such as unusual vaginal discharge, rashes in the genital area and pain during urination. Therefore it is particularly important to pay attention to painful urination if it occurs.
A more detailed account of STIs, their symptoms, diagnosis and management may be found here.